Convolutional Neural Network-Based Framework for the Detection of Tuberculosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58190/imiens.2025.153Keywords:
chest X-ray, computer-aided diagnosis, Convolutional Neural Networks, machine learning, tuberculosis detectionAbstract
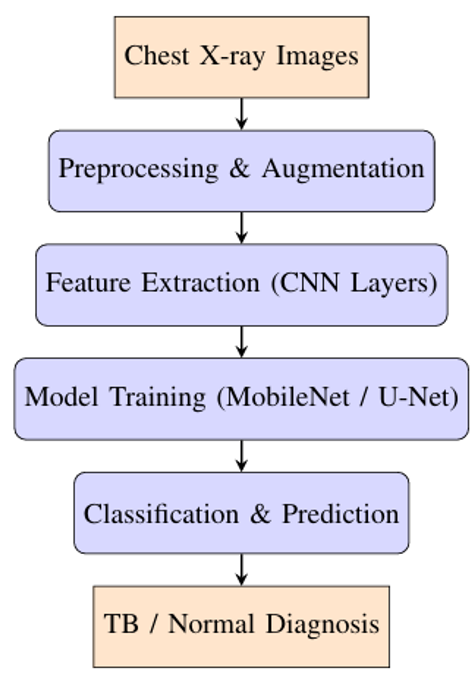
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant public health issue worldwide, especially in low- and middle-income countries, where access to accurate and rapid diagnostic tools is limited. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to control spread and improve patient outcomes. Traditional TB diagnosis methods, such as sputum microscopy and culture, are time consuming and require specialized laboratory facilities. In this study, we explored the application of machine learning techniques in automating and enhancing TB detection, focusing on the analysis of chest radiograph images (X-ray). Hence, a Convolutional Neural Network-based framework is presented. The framework used advanced image preprocessing and augmentation techniques to enhance feature learning and mitigate data set imbalance to support early screening and clinical decision making. The system demonstrated high precision, correctly identifying 97% of normal chest x-rays and achieving a perfect 100% precision for TB cases, which means no false positives were recorded. In terms of recall, the model correctly detected all normal X-rays but misclassified 5% of TB cases as normal, resulting in a 95% recall for TB detection. The F1-score, which balances precision and recall, was 98% for both normal and TB cases, indicating strong classification performance. Additionally, the macro and weighted averages were both 98%, reflecting consistent and reliable model performance across different case distributions. The results indicate that the proposed CNN-based framework provides a robust, scalable, and cost-effective solution for automated TB detection, offering potential integration into computer-aided diagnostic systems.
Downloads
References
[1] M. J. Friedrich, "Tuberculosis update 2017," JAMA, vol. 318, p. 2287, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.18477.
[2] C. L. Daley, "The global fight against tuberculosis," Thorac. Surg. Clin., vol. 1, pp. 19-25, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2018.09.010.
[3] A. Buzimkic, D. E. Heck, and H. D. Kim, "Risk management of infectious disease using multidimensional omics: Molecular diagnostic and personal care of tuberculosis," GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci., vol. 15, pp. 01–04, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.30574/gscbps.2021.15.1.0071.
[4] P. Anirvan, "The dire struggle: India’s unfulfilled promise to eliminate tuberculosis," Indian J. Med. Ethics, vol. 9, Sep. 2024, doi: 10.20529/IJME.2024.060.
[5] H. Karim, Z. College, R. Khan, D. Hafiz, U. Farooq, and F. Khatoon, "Global epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward achieving global targets," NeuroQuantology, pp. 5–1366, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.48047/nq.2023.21.5.NQ222124.
[6] M. Khan, N. Islam, J. Ferdous, and M. M. Alam, "An overview on epidemiology of tuberculosis," Mymensingh Med. J., vol. 28, pp. 259–266, Jan. 2019. [Online]. Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30755580/
[7] J. Yayan, K.-J. Franke, M. Berger, W. Windisch, and K. Rasche, "Early detection of tuberculosis: a systematic review," Pneumonia, vol. 16, Jul. 2024, doi: 10.1186/s41479-024-00133-z.
[8] T. Campelo, P. Sousa, L. Nogueira, C. Frota, and P. Antas, "Revisiting the methods for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis: what has the new millennium brought thus far?" Access Microbiol., vol. 3, p. 000245, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000245.
[9] S. Jaeger, S. Candemir, S. Antani, Y.-X. Wang, P.-X. Lu, and G. Thoma, "Two public chest x-ray datasets for computer-aided screening of pulmonary diseases," Quant. Imag. Med. Surg., vol. 4, pp. 475–477, Dec. 2014, doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.11.20.
[10] H. Mayanja-Kizza and A. Katamba, "Interferon-γ release assays or tuberculin skin test for latent tuberculosis infection?" Lancet Infect. Dis., vol. 20, pp. 1359-1360, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30363-7.
[11] N. Nilawati and B. Syam, "Effectivity strategy screening covid-19: Systematic review," J. Aisyah: J. Ilmu Kesehatan, vol. 6, pp. 71-74, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.30604/jika.v6iS1.763.
[12] A. Yasseen and S. Yuhaniz, "Automatic extraction of knowledge for diagnosing covid-19 disease based on text mining techniques: A systematic review," Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN), vol. 9, pp. 918–929, May 2021.
[13] T. Rahman et al., "Tb-cxrnet: Tuberculosis and drug-resistant tuberculosis detection technique using chest x-ray images," Cogn. Comput., vol. 16, pp. 1393–1412, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1007/s12559-024-10259-3.
[14] N. Rozali and A. Mustikarini, "What are the comparative diagnostic accuracies of x-ray, ct, and ultrasound in terms of sensitivity and specificity for detecting pulmonary tuberculosis in adult patients with suspected infection?: A systematic review," Int. J. Med. Sci. Health Res., vol. 12, pp. 95–135, May 2025, doi: 10.70070/m242mm34.
[15] M. Yeasmin, M. Amin, T. Joti, Z. Aung, and M. Azim, "Advances of ai in image-based computer-aided diagnosis: A review," Array, vol. 23, p. 100357, Sep. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.array.2024.100357.
[16] I. Mienye, T. Swart, G. Obaido, M. Jordan, and P. Ilono, "Deep convolutional neural networks in medical image analysis: A review," Information, vol. 16, p. 195, Mar. 2025, doi: 10.3390/info16030195.
[17] A. B. Rashid and M. A. K. Kausik, "Ai revolutionizing industries worldwide: A comprehensive overview of its diverse applications," Hybrid Adv., vol. 7, p. 100277, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.hybadv.2024.100277.
[18] B. S, P. Aruchamy, S. Kumar, and K. Venkatesh, "Medical Image Analysis Based on Deep Learning Approach for Early Diagnosis of Diseases," Mar. 2024, pp. 54–75, doi: 10.1201/9781003469605-4.
[19] M. Tripathi, "Analysis of convolutional neural network based image classification techniques," J. Innov. Image Process., vol. 3, pp. 100–117, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.36548/jiip.2021.2.003.
[20] Z. Saadi, A. Sadiq, O. Akif, and M. Eid, "Enhancing image classification using a convolutional neural network model," J. Soft Comput. Comput. Appl., vol. 1, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.70403/3008-1084.1010.
[21] P. Farnia, A. Velayati, J. Ghanavi, and P. Farnia, "Tuberculosis: An Ongoing Global Threat," in Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., vol. 1484, Nov. 2025, pp. 1-31, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-96883-9_1.
[22] P. Kolia-Diafouka et al., "Detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis in paucibacillary sputum: performances of the xpert mtb/rif ultra compared to the xpert mtb/rif, and is6110 pcr," Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., vol. 94, no. 4, pp. 365–370, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.02.008.
[23] R. Mandal and R. Pal, "Emerging technologies in tuberculosis diagnosis: A comprehensive review," Int. J. Pharm. Res. Dev., vol. 7, pp. 265–277, Apr. 2025, doi: 10.33545/26646862.2025.v7.i1d.119.
[24] A. Mirugwe, L. Tamale, and J Nyirenda, "Improving tuberculosis detection in chest x-ray images through transfer learning and deep learning: Comparative study of convolutional neural network architectures," JMIRx Med, vol. 6, Jul. 2025, doi: 10.2196/66029.
[25] X. Cao, Y. Li, H. Xin, H. Zhang, M. Pai, and L. Gao, "Application of artificial intelligence in digital chest radiography reading for pulmonary tuberculosis screening," Chronic Dis. Transl. Med., vol. 7, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2021.02.001.
[26] P. Sahoo, S. Sharma, S. Saha, D. Jain, and S. Mondal, "A multistage framework for respiratory disease detection and assessing severity in chest x-ray images," Sci. Rep., vol. 14, May 2024, doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60861-6.
[27] P. G. Lacaita et al., "The accuracy of chatgpt-4o in interpreting chest and abdominal x-ray images," J. Pers. Med., vol. 15, p. 194, May 2025, doi: 10.3390/jpm15050194.
[28] I. Ayebo and A. Johnson, "Medical image analysis with deep learning," Med. Image Anal., Dec. 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/390232925_Medical_Image_Analysis_with_Deep_Learning
[29] E. Oye and R. Lucas, "Convolutional neural networks (cnns)," Dec. 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/387278938_Convolutional_Neural_Networks_CNNs
[30] A. Khaliq et al., "Revolutionizing medical imaging: A cutting-edge ai framework with vision transformers and perceiver io for multi-disease diagnosis," Comput. Biol. Chem., vol. 119, p. 108586, Dec. 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2025.108586.
[31] I. Ahmad, J. Dai, Y. Xie, and X. Liang, "Deep learning models for ct image classification: a comprehensive literature review," Quant. Imag. Med. Surg., vol. 15, pp. 962–1011, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.21037/qi.
[32] T. Islam, M. S. Hafiz, J. R. Jim, M. M. Kabir, and M. Mridha, "A systematic review of deep learning data augmentation in medical imaging: Recent advances and future research directions," Healthc. Anal., vol. 5, p. 100340, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.health.2024.100340.
[33] M. Singh et al., "Evolution of machine learning in tuberculosis diagnosis: A review of deep learning based medical applications," Electronics, vol. 11, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.3390/electronics11172634.
[34] M. Mizan, M. A. Hasan, and S. Hassan, "A comparative study of tuberculosis detection using deep convolutional neural network," in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol. (ICAICT), Nov. 2020, pp. 157–161, doi: 10.1109/ICAICT51780.2020.9333464.
[35] N. Quang et al., "Deep learning models for tuberculosis detection from chest x-ray images," in Proc. 2019 Int. Conf. Inf. Commun. Technol. (ICT), Apr. 2019, pp. 381–385, doi: 10.1109/ICT.2019.8798798.
[36] S. Hansun et al., "A new ensemble transfer learning approach with rejection mechanism for tuberculosis disease detection," IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci., vol. PP, p. 1, May 2025, doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2024.3474708.
[37] S. Hansun et al., "Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence–based methods for tuberculosis detection: Systematic review," J. Med. Internet Res., vol. 27, p. e69068, Mar. 2025, doi: 10.2196/69068.
[38] P. Lakhani and B. Sundaram, "Deep learning at chest radiography: Automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks," Radiology, vol. 284, pp. 574-582, Aug. 2017, doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017162326.
[39] R. Hooda, A. Mittal, and S. Sofat, "Automated tb classification using ensemble of deep architectures," Multimedia Tools Appl., vol. 78, pp. 31515–31532, Nov. 2019, doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-07984-5.
[40] T. Sujatha and T. S. Reddy, "U-net segmentation for cnn classification to improve the accuracy of automatic prediction of brain tumors using mri images," J. Electr. Syst., vol. 20, pp. 2284–2295, Apr. 2024, doi: 10.52783/jes.2711.
[41] D. Capellán-Martín, J. J. Gómez-Valverde, D. Bermejo-Peláez, and M. J. Ledesma-Carbayo, "A lightweight, rapid and efficient deep convolutional network for chest x-ray tuberculosis detection," in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Biomed. Imag. (ISBI), Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230500.
[42] Z. Sadeghi et al., "A review of explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare," Comput. Electr. Eng., vol. 118, p. 109370, Aug. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109370.
[43] L. Vonderhaar, T. Elvira, and O. Ochoa, "An analysis of explainability methods for convolutional neural networks," Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 117, p. 105606, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105606.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Intelligent Methods In Engineering Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






