Effects of PSO Algorithm Parameters on the MPPT System Under Partial Shading Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58190/imiens.2023.8Keywords:
MPPT, photovoltaic, PV, PSO parameters, partial shading, solar energyAbstract
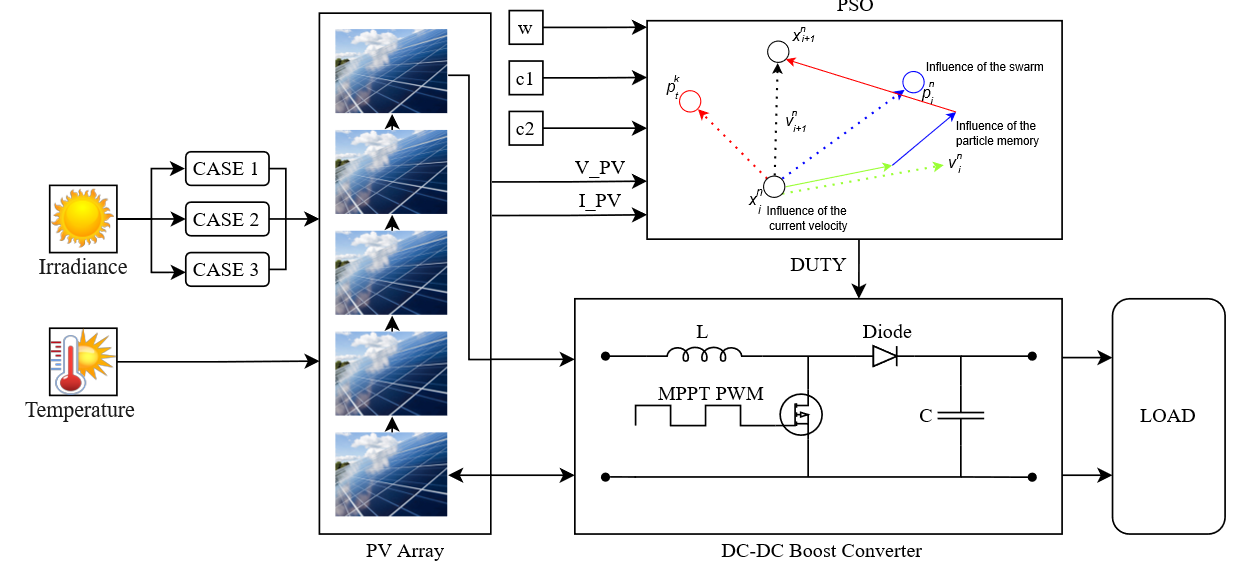
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) systems enable photovoltaic (PV) panels to work at their Maximum PowerPoint (MPP). To do this, several algorithms have been developed, including conventional, intelligent, and meta-heuristic. Once a partial shading condition (PSC) occurs, more than one peak emerges in the power-voltage curve of photovoltaic arrays. Under PSCs, conventional algorithms get stuck at the local maximum point and fail to reach the global maximum point. Being an alternative method, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm has been frequently employed for MPPT systems under PSCs. This algorithm has some parameters that affect its performance to reach the global MPP of the PV panel. Therefore, with well-tuned parameters, the effectiveness of the PSO will increase for the different PSCs. In this study, the effects of the cognitive learning and social learning parameters of the PSO algorithm are investigated under different PSCs. To achieve this, an MPPT system, including a boost-type DC-DC converter, is created in MATLAB®/Simulink®. Simulation studies show that the PSO algorithm fails to track global MPP with constant cognitive and social learning parameters under changing partial shading conditions. Furthermore, the results show that these two parameters affect the time to reach the MPP of the PSO algorithm.
Downloads
References
B. Özgenç and İ. H. Altaş, “Implementation of a new maximum power point tracking algorithm for partially shaded PV systems,” in Proc. 2019 7th International Istanbul Smart Grids and Cities Congress and Fair (ICSG), pp. 119–123, 2019.
A. Ramaden, and I. A. Smadi, “Partial shading detection and global MPPT algorithm for PV system,” in Proc. 2019 IEEE Jordan International Joint Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Technology (JEEIT), pp. 135–140, 2019.
A. O. Baba, G. Liu, and X. Chen, “Classification and evaluation review of maximum power point tracking methods,” Sustainable Future, vol. 2, pp. 100020, Jan. 2020.
A. R. Reisi, M. H. Moradi, and S. Jamasb, “Classification and comparison of maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic system: A review,” Renew. and Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 19, pp. 433–443, Mar. 2013.
R. B. A. Koad, A. F. Zobaa, and A. El-Shahat, “A novel MPPT algorithm based on particle swarm optimization for photovoltaic systems,” IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 468–476, 2017.
H. Chaieb and A. Sakly, “Comparison between P&O and PSO methods based MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems,” in Proc. 2015 16th International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA), pp. 694–699, 2015.
M. Azab, “Optimal power point tracking for stand-alone PV system using particle swarm optimization,” in Proc. 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, pp. 969–973, 2010.
P. T. Sawant and C. L. Bhattar, “Optimization of PV system using particle swarm algorithm under dynamic weather conditions,” in Proc. 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing (IACC), pp. 208–213, 2016.
A. F. Sagonda and K. A. Folly, “Maximum power point tracking in solar PV under partial shading conditions using stochastic optimization techniques,” in Proc. 2019 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Wellington, pp. 1967–1974, 2019.
S. Obukhov, A. Ibrahim, A. A. Zaki Diab, A. S. Al-Sumaiti, R. Aboelsaud, “Optimal performance of dynamic particle swarm optimization based maximum power trackers for stand-alone PV system under partial shading conditions,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 20770–20785, Jan. 2020.
M. Abdulkadir, A. H. M. Yatim, S. T. Yusuf, “An improved PSO-based MPPT control strategy for photovoltaic systems,” Int. J. Photoenergy, pp. 1–11, Jan. 2014.
K. H. Chao, Y. S. Lin and U. D. Lai, “Improved particle swarm optimization for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic module arrays,” Appl. Energy, vol. 158, pp. 609–618, Nov. 2015.
Y. H. Liu, S. C. Huang, J. W. Huang, W. C. Liang, “A particle swarm optimization based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions,” IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 1027–1035, Oct. 2012.
K. L. Lian, J. H. Jhang, and I. S. Tian, “A maximum power point tracking method based on perturb-and-observe combined with particle swarm optimization,” IEEE J. Photovoltaics, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 626–633, Jan. 2014.
S. M. Mirhassani, S. Z. M. Golroodbari, S. M. M. Golroodbari, S. Mekhilef, “An improved particle swarm optimization based maximum power point tracking strategy with variable sampling time,” Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 64, pp. 761–770, Jan. 2015.
M. Mao, L. Zhou, Z. Yang, Q. Zhang, C. Zheng, B. Xie, et al, “A hybrid intelligent GMPPT algorithm for a partial shading PV system,” Control Eng. Pract., vol. 83, pp. 108–115, Feb. 2019.
Y. Soufi, M. Bechouat, S. Kahla, “Fuzzy-PSO controller design for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic system,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, vol. 42, no.13, pp. 8680–8688, Mar. 2017.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Intelligent Methods In Engineering Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






